SCR denitration principle
The SCR (selective catalytic reduction) technique is to inject a reducing agent (ammonia or ammonia water) into an SCR reactor having a temperature range of 300 to 420 ° C in the presence of a catalyst and oxygen, selectively in the exhaust gas. NOx reduction produces N2 and H2O to reduce NOx.

The main reactions are as follows:
4NO+4NH3+O2=4N2+6H2O
4NH3+2NO2+O2=3N2+6H2O
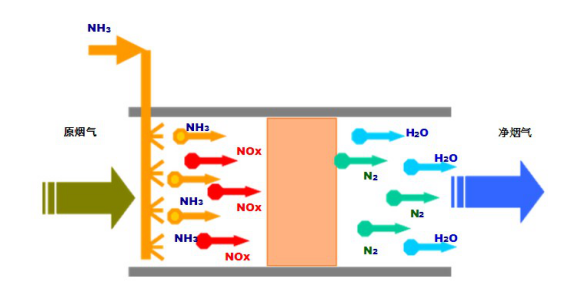
SCR denitration system consists of:
SCR denitration system mainly includes: reducing agent storage system, reducing agent delivery / metering system, reactor and external frame structure, denitration catalyst, soot box and electronic control system.

The SCR denitration reactor fully considers the characteristics of various boiler systems, and adopts a unique arrangement to efficiently and stably remove nitrogen oxides from the flue gas, which can minimize the clogging, wear and poisoning of the catalyst by the soot and increase the catalyst. The service life, which reduces operating costs, can carry different types of catalysts. A new type of catalyst, which uses ultrafine TiO2 as the substrate, vanadium oxide as the active component, tungsten, molybdenum and other oxides as additives, has high activity, high denitrification efficiency, strong anti-poisoning performance, wear resistance, and use. Long life and other characteristics. The typical SCR denitration process flow chart is as follows:
Denitration catalyst:

The catalyst on the SCR denitration system causes the reducing agent to selectively react with the nitrogen oxides in the flue gas at a certain temperature in the SCR reaction. At present, SCR catalysts are basically based on TiO2, with V2O5 as the main active ingredient, and WO3 and MoO3 as the antioxidant and anti-toxic auxiliary components.
Denitration catalyst monomer

Denitration catalyst module
